Database Systems
Relational Models
Relational Models
Table of Contents
Definitions
- data model: transforms real world objects into structures a computer can
store
- many approaches: relational, ER, object-oriented, network, hierarchical, …
- relational model:
- rows (Tuples/records)
- columns (attributes/fields)
- primary keys and foreign keys to link relations
- relational database: set of relations
- relation: consists of schema + instance
- schema: name of relation plus name and type of each attribute
- instance: table with rows and columns
- cardinality: number of rows
- degree/arity: number of fields
- consider relation a set of rows/tuples
- all rows are distinct and unordered
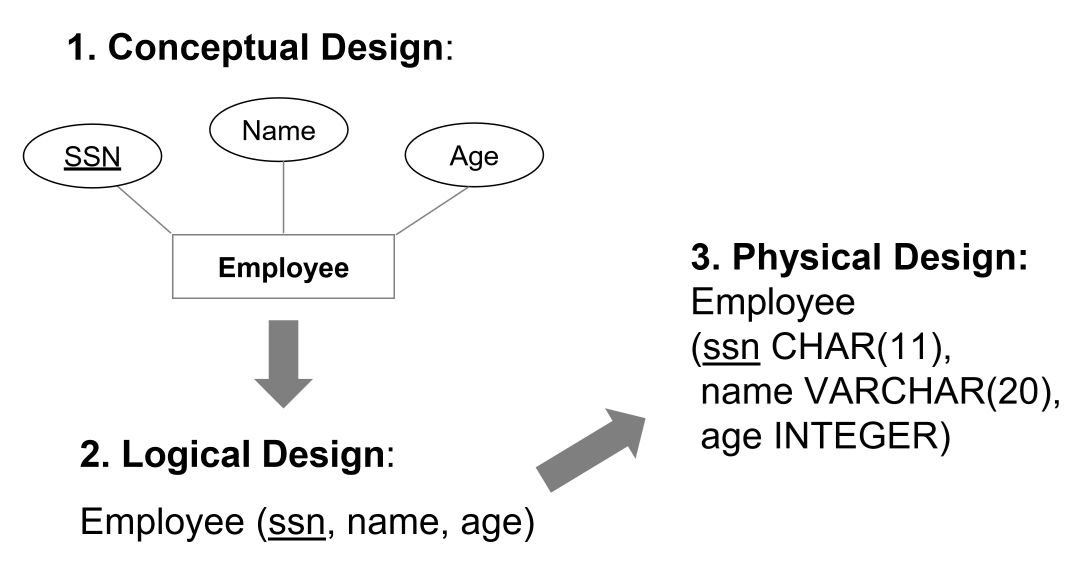
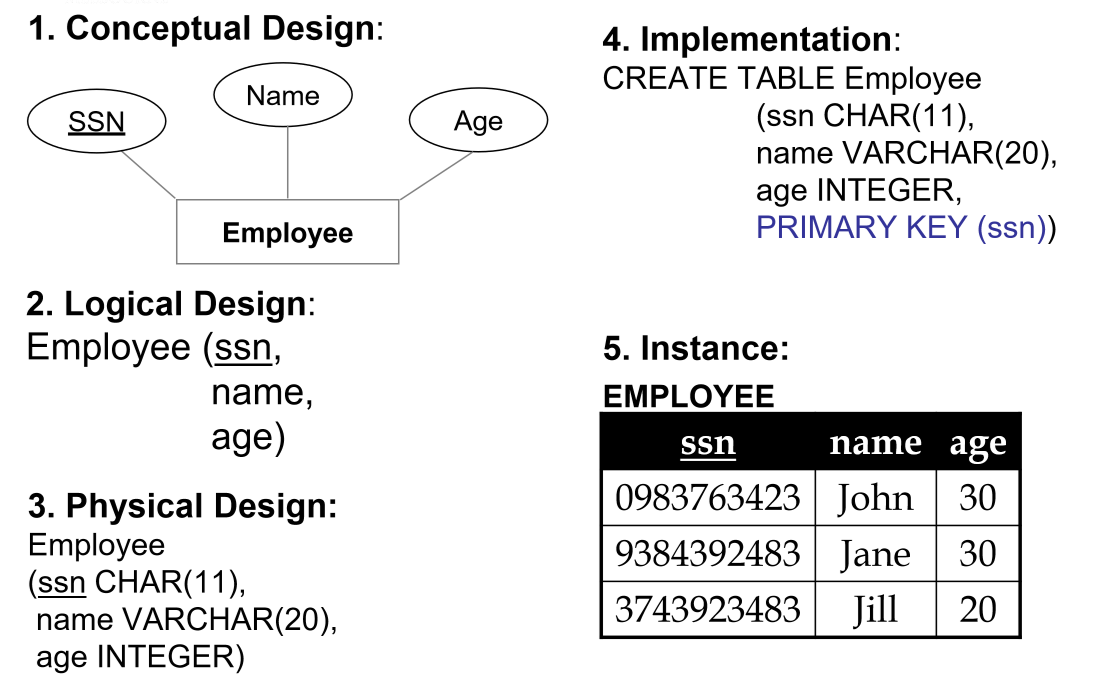
- logical design: entity set $\rightarrow$ relation
- physical design: select data types
Keys
- keys associate tuples/rows in different relations
- integrity constraint [TODO]
- superkey: set of fields used to uniquely identify a record
- key: minimal subset that uniquely identifies a record
- set of fields for a relation if it is a superkey and no subset is a superkey
- primary key: key chosen
- others are candidate keys
- every relation has a primary key
- `PRIMARY KEY (
)
- foreign key: set of fields in one relation used to refer to a tuple/row in
another relation
- must correspond to primary key of other relation
- referential integrity: implies all foreign key constraints are enforced in
DBMS
FOREIGN KEY (<key>) REFERENCES <table>- i.e. referenced tuple exists in referenced table
- can define behaviour on tuple deletion: disallow deletion of referenced object, cascade deletion through relations that reference the object, …
Integrity Constraints
- integrity constraint: condition must be true for any instance of
database
- e.g. domain constraints
- ICs specified when schema defined
- ICs checked when relations modified
- legal instance $\iff$ all specified ICs satisfied
- DBMS should not allow illegal instances.
Logical Design
Multi-valued Attributes
- multi-valued attributes: options
- unpack/flatten when converting to logical design
- otherwise create a lookup table
- e.g. multiple phone numbers for an employee $\Rightarrow$ (home_num, work_num)
Composite Attributes
- e.g. address: flatten by breaking into components (postcode, street name, street num)
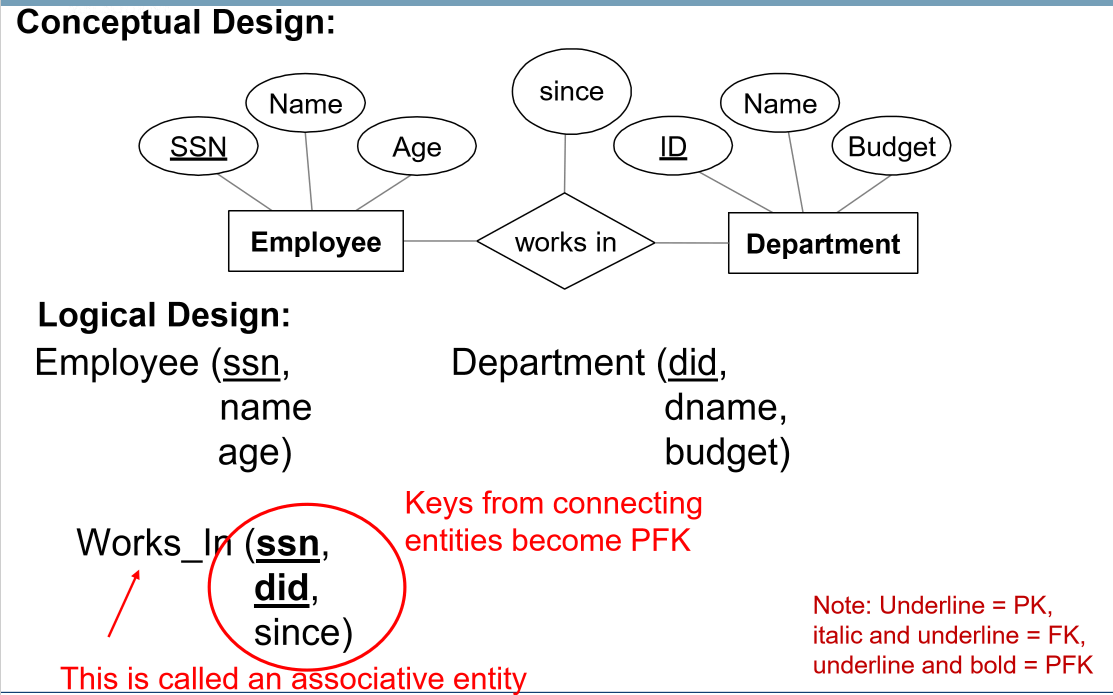
Many-to-many relationships
- many-to-many relationship $\rightarrow$ relation
- attributes include:
- keys for each participating entity set (as foreign keys)
- set of attributes forms superkey of relation
- all descriptive attributes
- keys for each participating entity set (as foreign keys)
- attributes include:
Ternary Relationships
[TODO]
Key constraints rule
- primary key from the many side becomes a foreign key on the one side
- ensures key constraint holds
Participation constraints
- total participation is specified with key words
NOT NULL, i.e. this field cannot be empty - every time you specific an attribute you need to indicate whether
NULLorNOT NULL
Translating weak entities
- weak entity set and identifying relationship set are translated to a single table
- when owner is deleted, all owned weak entities must be deleted