Database Systems
Conceptual Design
Conceptual Design
Table of Contents
[ ] Ch 2 R&G
Objectives of Conceptual design
- identify entities and relationships
- identify information to store about entities and relationships
- identify integrity constraints
Entities and Relationships
- entity: real-world object distinguishable from other objects
- entity set: collection of entities of the same type
- need not be disjoint
-
set of $n$-tuples: ${(e_1, \ldots, e_n) e_1 \in E_1, \ldots, e_n \in E_n}$ - each $n$-tuple involves $n$ entities $e_i$ in entity set $E_i$
- attributes: describe each entity in a given entity set
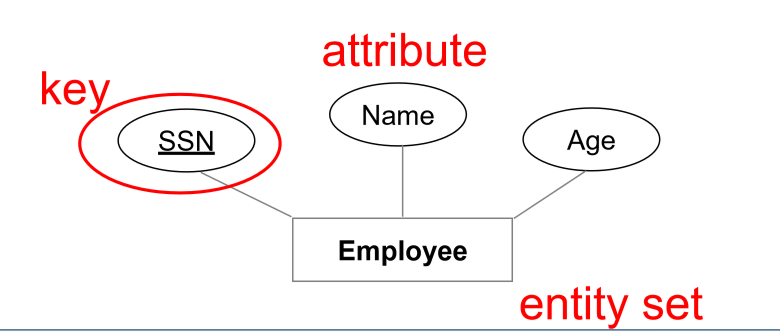
- relationship: association among two or more entities
- can have their own attributes
- e.g. Fred works in pharmacy department
- relationship set: collection of relationships of the same type
- e.g. employees work in departments
- instance of relationship set: snapshot of relationship set in time
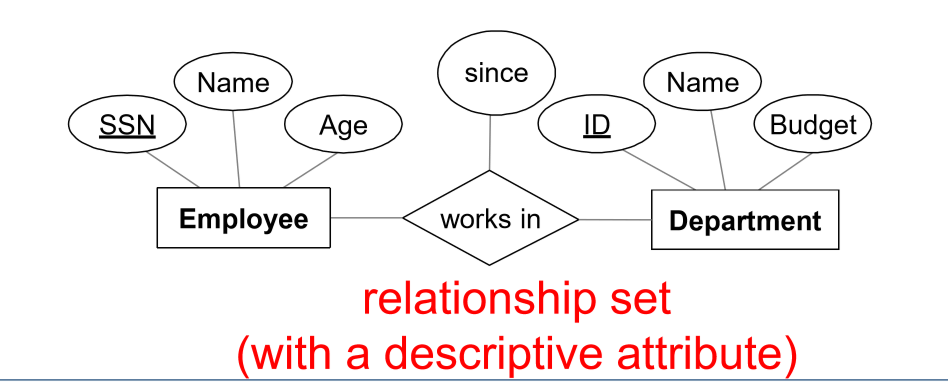
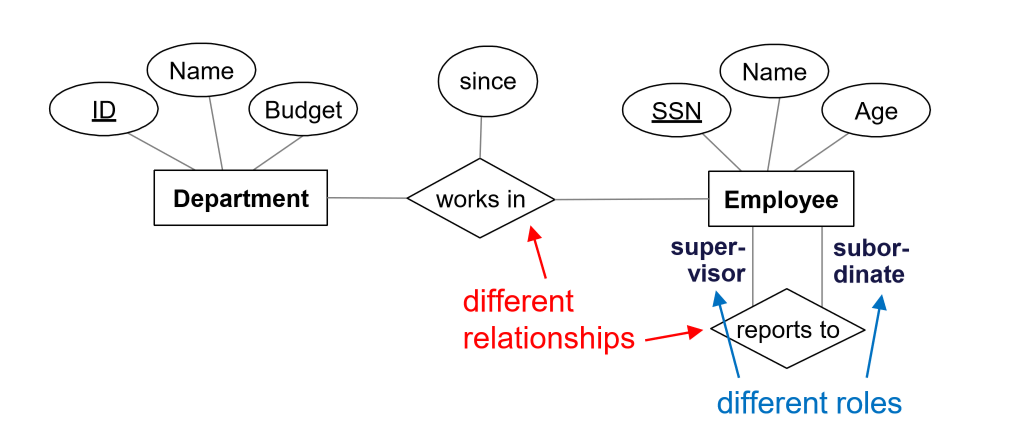
- same entity set can participate in
- different relationship sets
- different roles in the same set
- entity-relationship (ER) data model: tools to move from informal user needs to precise description that can be implemented
Constraints
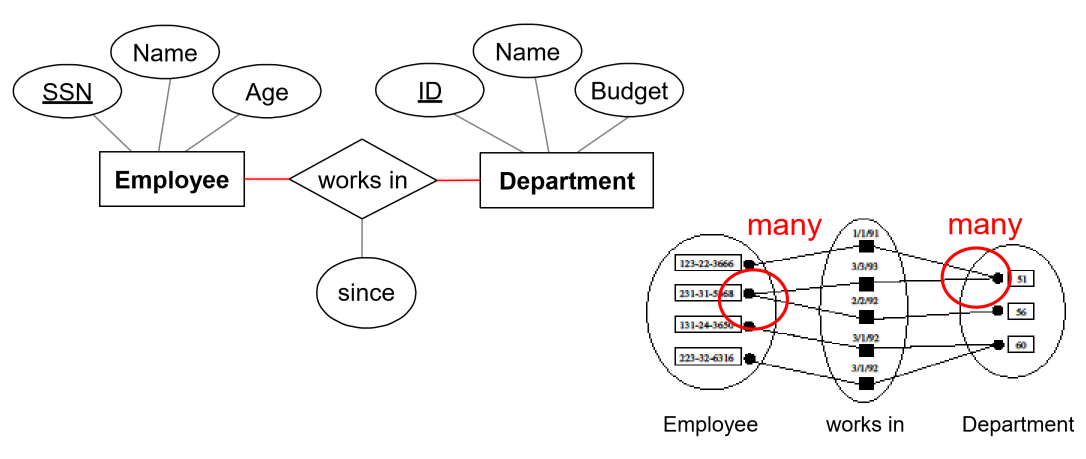
- key constraints: determine number of objects taking part in relationship set
- specifies upper bound, i.e. many implies you could have 0 relationships to more than 1
- one of:
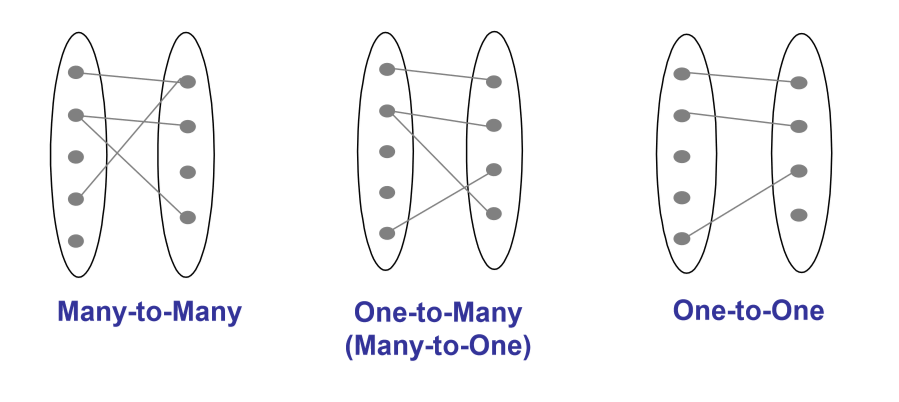
- many-to-many: employee can work in many departments; a department can have many employees
- represented by a line
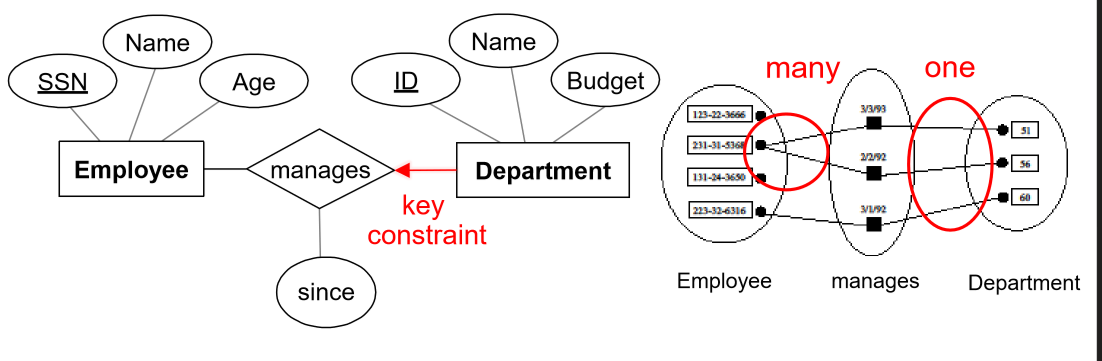
- one-to-many: single entity per relationship
- represented by an arrow
- e.g. each department has at most one manager
-
one-to-one: e.g. each employee can manage at most one department
-
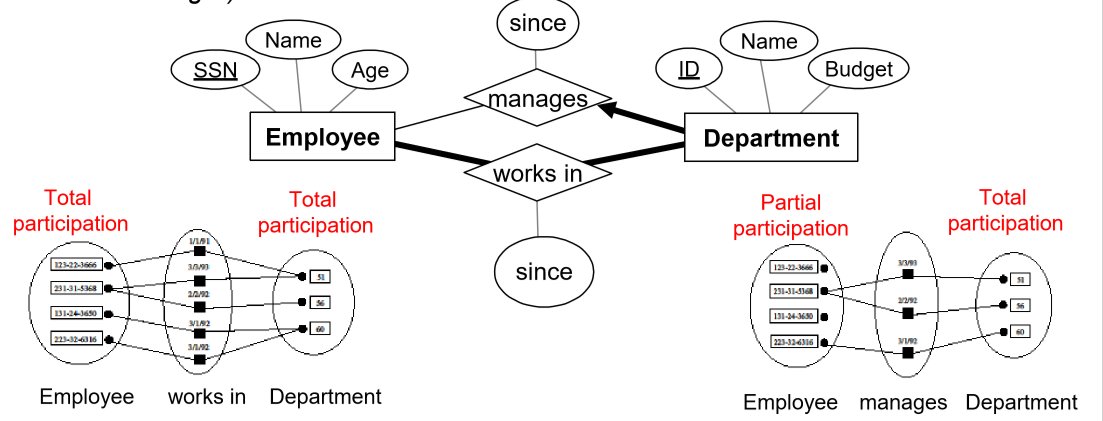
participation constraint: do all entities of an entity set take part in a particular relationship?
- total participation: every entity must take part in at least 1 relationship
- represented by a bold line
- partial participation: otherwise
- e.g. every employee must work in a department. each department has at least one employee each department has to have a manager (but not everyone is a manager)
- total participation: every entity must take part in at least 1 relationship
- weak entity: uniquely identified by considering primary key of an owner entity
- represented as bold rectangle
- owner entity set and weak entity set must participate in a relationship where each weak entity has exactly one strong entity to depend on
- partial key uniquely identifies weak entity when considering primary key of owner entity
- represented with dashed underline
| Key constraint | Total participation | Partial participation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | one-to-one | 0-to-one |
| many | one-to-many | 0-to-many |
- ternary relationships [TODO]
Special attribute
- multi-valued attributed: multiple values of same type
- e.g. employee home phone and work phone numbers
- represented with oval with double border
- composite attributes: hidden structure, each element having different type
- e.g. employee address composed of postcode, street name, street number