Computer Systems
Operating System Examples
Operating System Examples
Table of Contents
Windows NT
Wiki: Windows NT
- family of operating systems
- processor-independent, multiprocessing, multi-user OS
- initially produced for workstations and servers
- eventually expanded into general purpose OS for all PCs, deprecating Windows 9x family
- “NT”: originally New Technology
- written in C (kernel mode code) and C++ (user mode code)
- goals: hardware, software portability
- features:
- Hyper-V: native hypervisor
- Hardware Abstraction layer: set of routines in software providing programs
with access to hardware through programming interfaces
- BitLocker: full volume encryption feature, using AES in CBC mode
- NTFS: journaled, secure file system
Wiki: Architecture
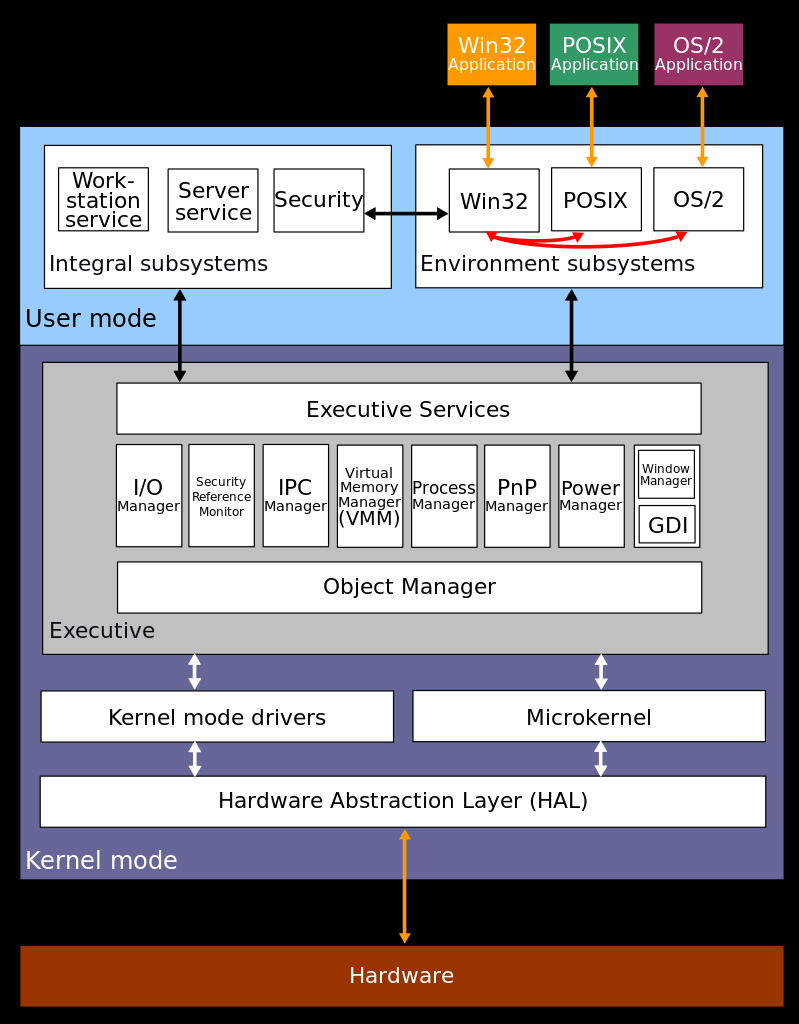
OS Properties
- preemptive: processes can be suspended without their cooperation, returning control
to the OS
- reentrant: ability of code to be executed 2+ times simultaneously
- in a multiprocessor there is the chance a CPU will start executing it at the
same time as another, meaning threads could be executing the same code at the
same time. Protect against with mutexes etc to protect critical regions
- in a uniprocessor: a procedure could be invoked in the middle of execution
of the same procedure. It is possible that the data structure the new procedure
is access was left in an inconsistent state by the interrupted procedure
- consider scheduling manager: if this was updating the queue, which gets interrupted
partway through. The scheduler is called and encounters an inconsistent queue,
causing it to crash
- multitasking: concurrent execution of multiple tasks
